As enterprise adoption of generative AI surges, forward-thinking CISOs and security leaders are recognizing a critical blind spot. Tools like ChatGPT, Bard, and custom large language model (LLM) applications are being rapidly integrated into workflows – but traditional firewalls and security controls don’t understand AI prompt interactions. This means sensitive data could slip out or malicious instructions could slip in, all under the radar of legacy defences. In response, a new breed of security solution has emerged: the generative AI firewall. This article explores what a generative AI firewall is, how it works, and why enterprises may need this generative AI firewall solution to securely embrace the GenAI revolution.
The Generative AI Security Gap in Enterprises
Generative AI’s meteoric rise has left enterprises scrambling to manage its risks. ChatGPT famously reached 100 million users just two months after launch – the fastest growing app in history. Employees are eagerly leveraging AI for productivity, sometimes pasting confidential code or data into prompts. Unfortunately, this has already led to high-profile incidents: for example, Samsung had to ban employees from using ChatGPT after engineers accidentally leaked sensitive source code to the AI. Financial institutions like JPMorgan and Goldman Sachs similarly restricted AI chatbot use over fears that sensitive information could be exposed, potentially violating regulations. These reactions underscore a key point: organizations fear what they can’t see or control in AI interactions.
Traditional security tools offer limited help here. Standard network firewalls and web application firewalls (WAFs) inspect packets and web requests, but they cannot inspect the content of AI prompts and responses. A conventional WAF is ill-equipped to handle the unique challenges of GenAI – threats like prompt injections, AI hallucinations, or data leakage simply aren’t on its radar. Even built-in model safeguards (like OpenAI’s filters or Meta’s Llama Guardrails) are not foolproof. In fact, researchers found that popular LLMs could be “jailbroken” with a 62% success rate on average, bypassing their safety measures. This means an attacker or even a well-intentioned user could manipulate an AI model to produce disallowed outputs or reveal confidential data, despite the model’s internal protections.
All these factors create a perfect storm of risk: enterprise data might be inadvertently leaked through AI, malicious actors might exploit AI systems via crafty inputs, and compliance/governance teams have zero visibility into what questions employees are asking or what answers they’re receiving. This security gap is driving demand for solutions that can monitor and control generative AI usage without stifling innovation. Enter the Generative AI Firewall.
What Is a Generative AI Firewall?
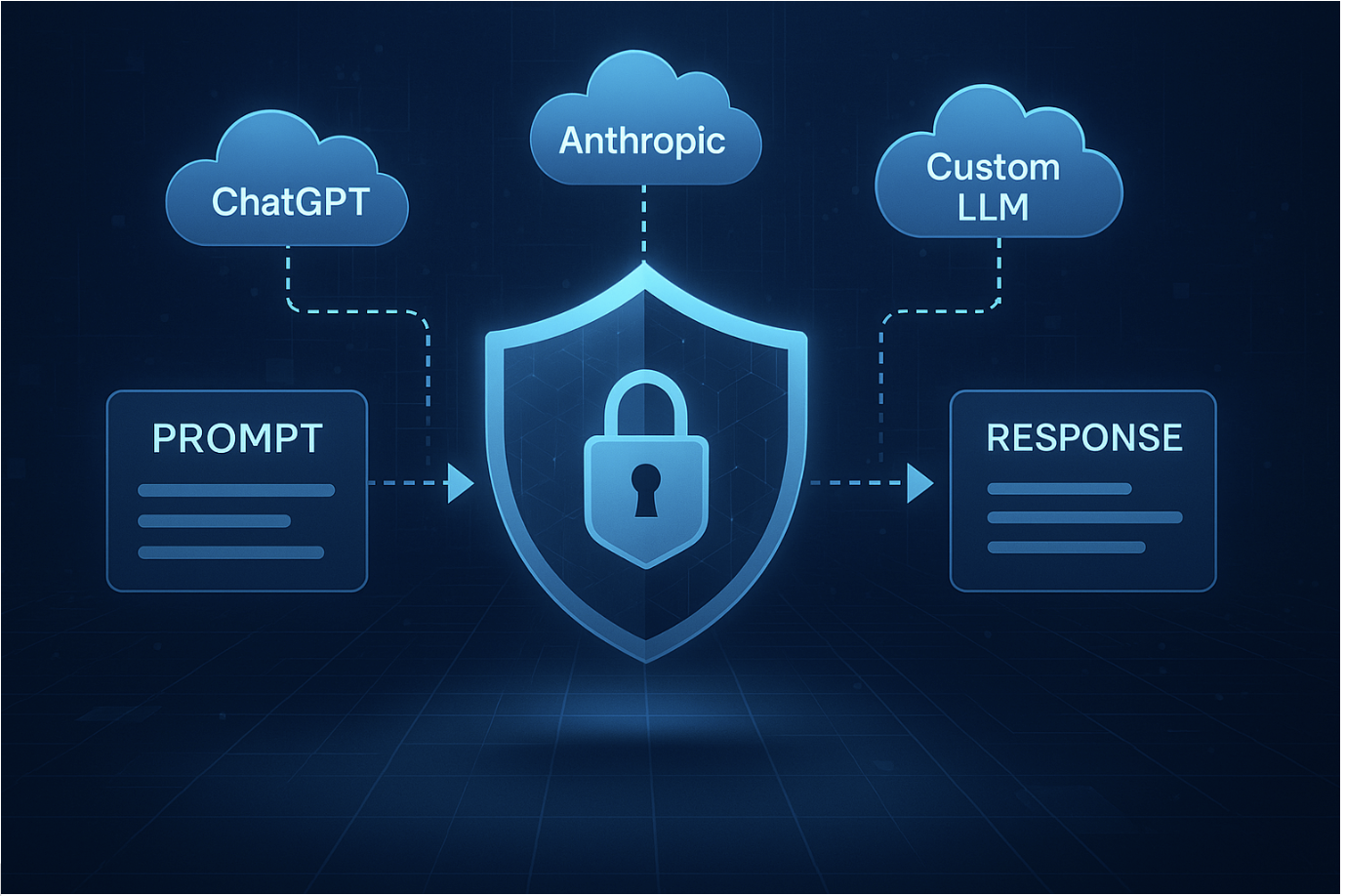
A Generative AI Firewall (also called an LLM firewall or AI application firewall) is a security system designed specifically to protect interactions with large language models and other generative AI. In essence, it acts as a smart intermediary between users (or applications) and the AI model. Instead of just monitoring network ports or URLs, an AI firewall inspects the content of AI prompts and the model’s responses, enforcing policies to prevent misuse and data exposure. It’s analogous to a web application firewall, but purpose-built for the peculiarities of generative AI conversations.
Traditional firewalls focus on network traffic, whereas a generative AI firewall focuses on prompt/response traffic – the actual text going into and out of an AI model. This context-aware approach allows it to understand what the user is asking the AI, and what the AI is replying with, in order to apply security rules. Notably, an AI firewall can operate at multiple stages of an AI interaction. For example, it can sit in front of the AI model to sanitize incoming prompts (blocking malicious or forbidden instructions) and also evaluate outgoing model responses (filtering out sensitive data or toxic content before it reaches the user). Advanced solutions may even insert themselves into the AI’s retrieval process (for AI systems that fetch data from knowledge bases) to prevent indirect prompt injections or data poisoning.
Crucially, a generative AI firewall is policy-driven and context-aware. According to AI security experts, these firewalls come with built-in policies covering things like sensitive data exposure, inappropriate content/tone, off-topic queries, phishing attempts, and known AI attack patterns. They act as a protective barrier for AI systems, guarding against both external threats and careless or malicious internal use. If a user prompt violates a policy (say, it contains a social security number, or attempts a known “jailbreak” phrase), the firewall can take action – such as redacting the sensitive info, blocking the query or response, or even terminating the session. Similarly, if the AI’s response contains something forbidden (e.g. confidential data or hate speech), the firewall can intercept and prevent that from ever reaching the end user.
In summary, a generative AI firewall extends the familiar concept of a firewall into the realm of AI-driven communication. It monitors and controls AI inputs and outputs in real time to enforce security, privacy, and compliance requirements that traditional defences simply don’t cover. This new category of security tool has quickly become a cornerstone of “AI security” architectures for organizations looking to harness AI benefits without inviting AI-related disasters.
How Does a Generative AI Firewall Work?
Implementing an AI-aware firewall requires a combination of natural language processing, content filtering, and integration with AI systems. Different vendors’ solutions vary, but most generative AI firewalls provide a core set of capabilities designed to tackle the major GenAI threats. Below are key features and how they work:
- Prompt Injection Protection: The firewall monitors and filters incoming user prompts to detect malicious instructions or injection attacks, blocking them before they ever reach the LLM. This might involve scanning prompts for known exploit patterns (like attempts to bypass safeguards with “ignore previous instructions” tricks) and using AI itself to evaluate the intent of each prompt. By sanitizing prompts, the firewall preserves the integrity of the AI’s behaviour.
- Sensitive Data Leakage Prevention: A generative AI firewall acts as a form of data loss prevention (DLP) for AI. It examines both user queries and AI-generated answers to spot any confidential or regulated data (source code, PII, financial records, etc.) and blocks or redacts such data if detected. This prevents users from accidentally leaking intellectual property to an AI service, and conversely stops an AI from revealing secrets it was trained on. In effect, the firewall enforces your data classification policies on AI conversations.
- Content Moderation and Output Validation: Advanced AI firewalls perform content moderation on the model’s outputs, similar to how an email filter might scan for inappropriate language. They check that the LLM’s responses are on-topic, accurate, and compliant with ethical and company guidelines. Dangerous content like hate speech, self-harm advice, or blatantly false “hallucinations” can be flagged and removed. The firewall may also validate facts in the response (for example, cross-checking against a trusted data source) especially in retrieval-augmented generation scenarios, to catch misinformation before it spreads.
- Jailbreak Detection and Guardrails: Many solutions include specialized techniques to detect and thwart “jailbreak” attempts – situations where users try to trick the AI into ignoring its safety rules. For instance, cloudsineAI’s ShieldPrompt™ technology embeds hidden “canary” prompts in the system message, which should never be revealed; if a user prompt causes the model to output a canary token, the firewall knows a system instruction was accessed and can flag a potential jailbreak. Other methods like tokenization tricks (e.g. Byte Pair Encoding with random dropout) are used to confuse prompt injection scripts. These multilayered guardrails ensure the AI stays within its allowed behaviour boundaries.
- Rate Limiting and Abuse Prevention: To maintain system reliability, a generative AI firewall often implements user input rate limiting and usage quotas. This prevents both malicious actors and overeager users from overloading the AI with an excessive volume of requests (an AI-specific denial-of-service angle). It also helps control costs in pay-per-use AI models by curbing unbounded consumption. By throttling or blocking unusually high request rates, the firewall can stop automated attacks or data scraping attempts without human intervention.
- Logging and Audit Trails: Every prompt and response that flows through the AI firewall can be logged and audited. This is a critical but often overlooked feature. Comprehensive logs mean that Security Operations Center (SOC) analysts can review AI interactions for signs of misuse or data exfiltration after the fact, and compliance officers can demonstrate adherence to policies. For example, if an employee tried to paste a client’s credit card number into an AI prompt, the attempt would be logged (and likely blocked), providing an audit trail for compliance. These logs can feed into SIEM/SOC monitoring tools, giving security teams much-needed visibility into AI usage patterns.
- Policy Configuration and Integration: Finally, a generative AI firewall comes with a management interface or security portal for administrators to define policies and view insights. Security teams can configure granular rules – for instance, disallowing any prompts related to certain sensitive projects or enforcing that no AI response may contain personal data. The firewall integrates with existing infrastructure: it can sit in front of internal LLM apps or serve as a proxy to external AI APIs, and often integrates with identity management (to apply user-specific policies) and with incident response workflows. Leading solutions align with industry frameworks like the new OWASP Top 10 for LLMs and NIST’s AI Risk Management Framework to ensure a comprehensive defence posture.
In practice, deploying a generative AI firewall means inserting this control layer wherever AI is used. If you have a custom GenAI application (say a customer support chatbot or an AI coding assistant), the firewall would be deployed in-line – for example, as a gateway that all user queries pass through on their way to the LLM model, and all responses pass through on the way back to the user. If employees are using external AI services (like ChatGPT’s web interface or API), an AI firewall can be implemented at the network level (as a secure proxy or cloud service) to intercept that traffic, or via browser extensions and plugins that route AI queries through the corporate filtering service. The goal is to embed AI-aware security checks into all channels where generative AI is accessed.
Why Enterprises Need a Generative AI Firewall Solution Now
Deploying a generative AI firewall may sound like an optional nice-to-have – until you consider the rapidly evolving threat landscape and regulatory environment around AI. Here are several compelling reasons why enterprise security and risk leaders are investing in this technology today:
- Preventing Data Leakage and IP Loss: Employees using generative AI without oversight can inadvertently become insider threats. They might input sensitive design documents or customer data into an AI prompt, not realizing that information could be retained or seen by the AI provider. Likewise, a sophisticated prompt injection attack might coax an AI to reveal proprietary training data (imagine an internal LLM spilling snippets of source code it was trained on). Traditional DLP systems may not catch these, but an AI firewall specifically blocks prompts or responses containing confidential data. This capability is a safety net that prevents costly data leaks, protecting intellectual property and privacy.
- Mitigating New AI-Specific Attacks: Security researchers and adversaries are actively probing LLMs for weaknesses. New categories of attacks – prompt injections, model poisoning, output manipulation – have no analogue in pre-AI software. For example, an attacker might craft a prompt that causes your customer-facing chatbot to output inappropriate content, damaging your brand, or to give faulty financial advice, causing compliance issues. An AI firewall provides robust, layered defences against prompt injection and similar exploits, ensuring the integrity of your AI applications. It can also detect anomalies like someone attempting hundreds of weird queries (maybe trying to find a vulnerability), and automatically curb that activity. Simply put, it closes the critical security gaps introduced by generative AI that legacy tools miss.
- Ensuring Regulatory Compliance and Ethical Use: Regulations around AI are tightening – from data protection laws (which cover how personal data is processed by AI) to emerging AI-specific regulations (like the EU AI Act) that will mandate risk controls. Even industry guidelines like the OWASP Top 10 for LLMs (2023) emphasize oversight for issues like data disclosure, misinformation, and misuse. A generative AI firewall helps organizations demonstrate compliance by enforcing policies and logging all AI interactions. For example, a compliance officer can set rules to ensure no AI-generated output violates harassment or discrimination policies (a key concern for HR and legal). If an audit or investigation occurs, the company can produce detailed logs of AI usage and prove that sensitive data was not mishandled. This kind of governance layer is quickly becoming essential for enterprise AI accountability.
- Safeguarding Brand and Customer Trust: AI-driven services often interface directly with customers (think of a chatbot on your banking app or an AI agent assisting with support). A mistake or malicious manipulation could be front-page news – such as an AI giving racist responses or leaking a customer’s account details. The generative AI firewall functions as a quality and safety gate, validating that responses are appropriate, accurate, and safe before they go out. It filters out toxic language and ensures the AI sticks to approved knowledge sources, which protects your brand reputation and prevents public relations nightmares. Internally, it also enforces that employees aren’t using AI to generate inappropriate content or code that violates company policy.
- Enabling Innovation with Confidence: Perhaps the biggest strategic reason for an AI firewall is that it lets you embrace AI innovation securely. Instead of outright banning AI tools (which some firms felt forced to do), organizations can allow and encourage AI use with guardrails in place. By transparently monitoring and controlling AI interactions, a generative AI firewall gives leadership the confidence that risks are managed. This means data scientists can integrate LLMs into products, and employees can leverage AI assistants, without security constantly worrying about the “what if” scenarios. In essence, the firewall becomes a key enabler for AI adoption, balancing the business benefits of GenAI with effective risk mitigation. As one AI security CEO put it, the goal is to “enable businesses to innovate confidently without compromising on security”.
Use Cases and Examples for SOC, Compliance, and Risk Teams
A Generative AI Firewall delivers value across multiple facets of enterprise security operations and risk management. Below are some concrete examples of how different teams can leverage this solution:
- Security Operations (SOC) Team: The SOC can integrate the AI firewall’s alerts and logs into their SIEM, getting real-time visibility into potentially dangerous AI activity. For instance, if a user attempts a known prompt injection exploit or if the AI returns a response with sensitive keywords, the firewall can generate an alert for the SOC to investigate. It can also automatically halt suspicious interactions (e.g. terminating a session if a user repeatedly tries to jailbreak the model). This turns AI usage into another monitored vector in the SOC’s threat landscape, complete with incident response playbooks for AI-related events. The SOC team thus gains the ability to detect and respond to AI-specific threats that would otherwise fly under the radar.
- Compliance and Data Governance: Compliance officers can define policies in the generative AI firewall that map to regulatory requirements – for example, no output should contain customer PII or PCI data, and no prompt should request something that violates privacy laws. The firewall’s ability to redact or block disallowed content ensures that the organization doesn’t breach regulations even inadvertently. All AI prompts and responses are logged with a timestamp and user ID, providing an audit trail. If an auditor inquires how your company prevents sensitive data from being sent to an external AI service, you can demonstrate that a control (the AI firewall) is in place and show records of its interventions. This is invaluable for meeting obligations in sectors like finance (e.g. SEC, FINRA rules) or healthcare (HIPAA) regarding data protection and oversight.
- Enterprise Risk Management: Risk officers look at the big picture of operational and strategic risks. A generative AI firewall helps reduce the risk of data breaches, legal liabilities, and business disruption stemming from AI. For example, consider the risk of an employee unwittingly exposing trade secrets to a public AI – the firewall mitigates that. Or the risk of relying on an AI that might produce fraudulent or biased output – the firewall’s validation and moderation reduce that risk. By deploying this control, risk managers can lower the residual risk associated with AI projects to an acceptable level, which in turn allows the business to pursue AI opportunities that might otherwise be deemed too risky. In risk assessments, the presence of an AI firewall can be documented as a key mitigation for several identified risk scenarios (data leakage, AI misuse, etc.), showing stakeholders that the company is proactively managing GenAI risks with the same rigor as cybersecurity and financial risks.
In each of these cases, the generative AI firewall serves as both a shield and an enabler. It shields the organization from the novel threats of AI, and enables various stakeholders to proceed with AI initiatives under a safety net.
cloudsineAI’s WebOrion® Protector Plus: A Purpose-Built GenAI Firewall
When evaluating generative AI firewall solutions, it’s important to look for a platform that covers the capabilities and use cases described above. One example is cloudsineAI’s WebOrion® Protector Plus, which is positioned as a GPU-powered GenAI firewall for mission-critical AI applications.
WebOrion® Protector Plus provides all the key features one would expect in a generative AI firewall: it prevents sensitive data leakage by examining prompts and responses, blocking any that contain confidential information; it has layered prompt injection defences to preserve the integrity of your AI’s outputs; it includes content moderation filters to ensure generated content stays within ethical and policy bounds; and it applies rate limiting to user queries to thwart abuse or runaway usage. These features map directly to the risks enterprises face – from preventing leaks of PII to stopping prompt-based exploits and toxic outputs.
What sets cloudsineAI’s solution apart is the contextual intelligence built into its ShieldPrompt™ engine. ShieldPrompt uses multiple techniques in tandem (as mentioned earlier: context evaluation via an LLM, canary tokens, adaptive prompt hardening, auto-generated guardrails) to achieve a high precision of threat detection. This means fewer false positives and a stronger ability to catch sophisticated attack attempts that simpler keyword-based filters might miss. The platform is also aligned with industry standards – it addresses the OWASP Top 10 for LLMs, and incorporates best practices from NIST and other AI security frameworks.
Another practical advantage is deployment flexibility. cloudsineAI offers the GenAI firewall as a hardware appliance, a cloud-delivered virtual appliance, or a SaaS model. This means whether your AI systems are on-premises, in the cloud, or you need to secure employee access to external AI services, there’s a deployment mode that fits. It can integrate with popular LLM platforms (from open-source models like Llama 2 to API services like OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, AWS Bedrock, etc.) as a gateway, making it a versatile overlay to whatever AI infrastructure you have. In short, cloudsineAI’s Protector Plus is designed to be an enterprise-grade GenAI firewall solution that plugs into your existing security environment and empowers you to adopt AI confidently and safely.
Conclusion
Generative AI is transforming business operations and competitive landscapes, but it also introduces unprecedented security and compliance challenges. A Generative AI Firewall is a strategic investment that allows enterprises to reap the rewards of AI while maintaining control over data and behaviour. By monitoring AI prompts and responses, detecting jailbreaking attempts, blocking sensitive data egress, and logging every interaction, this new class of security tool fills the critical gap left by traditional firewalls and cloud security solutions. In an era where an AI’s output can be as impactful as an employee’s action, putting a governance layer around AI is simply prudent risk management.
For forward-thinking CISOs, security architects, and IT directors, the question is not just “What is a Generative AI Firewall?” but also “Do we need one now?”. If your organization is building LLM-powered apps, and you care about data protection, compliance, and brand trust – then the answer is likely yes. A generative AI firewall solution can be the linchpin of your AI security strategy, ensuring that innovation does not come at the expense of security.
cloudsineAI understands these challenges deeply. The WebOrion® Protector Plus GenAI firewall was created to solve exactly these problems for enterprises like yours. It enables you to embrace AI-driven transformation safely and responsibly, with powerful protection working behind the scenes so you don’t have to choose between innovation and security. Take the next step in securing your AI future: Engage with cloudsineAI today and build a foundation of trust for all your GenAI initiatives.